Rich snippets allow search engines to better understand what information is contained on each web page. Major search engines have now gone much further, with relevant structured content drawn directly from your site and presented within the search result.
Typically when your website shows up on a search engine result, it displays the site title, URL and whatever meta description you have assigned to the page. When Rich snippets are implemented, Google is now able to display a bit more information about the actual result, including whether this particular result is a review, a person, a product, a business, and a lot more.
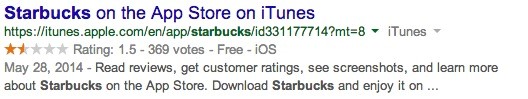
Typical search result:

Search result with review data in a rich snippet:
Rich Content Types
 Rich content types categorize your content for use with rich snippets but it also helps answer the question, “what do I put on my site?”, particularly when you are starting with little or nothing. It will help you plan for the people and resources you will need to produce content.
Rich content types categorize your content for use with rich snippets but it also helps answer the question, “what do I put on my site?”, particularly when you are starting with little or nothing. It will help you plan for the people and resources you will need to produce content.
For developers you can use the Structure Data Testing tool to make sure you are implementing correctly:
https://search.google.com/structured-data/testing-tool
Reviews – can be both individual or aggregate reviews. https://developers.google.com/search/docs/data-types/review
People – Google and Bing now show more information from LinkedIn when you search for people. Similar results are possible for any website that includes profiles of staff, team members and other people relevant to the business.
Products – one of the most important uses of structured data markup is for products and special offers from merchants, especially online stores. Name, image, brand, description, identifiers (ISBN, SKU, etc.) and reviews, all extendable with price, currency, seller, condition, and quantity. https://developers.google.com/search/docs/data-types/product
Businesses & Organizations – business name, address (physical and URL), telephone number, geolocation (latitude and longitude) and logo.
Local Business – When users search for businesses on Google Search or Maps, search results may display details about a business that matched the query. When users query for a type of business, such as a restaurant, they may see a carousel of listings hosted by restaurant listing providers.
Recipes – structured data markup for recipes offer a lot of options, allowing cooking and recipe collections to include everything from the type of dish, reviews, and preparation and cooking time, to nutritional information like serving size, calories, fat content and more. https://developers.google.com/search/docs/data-types/recipe
 Events – the usage of structured data markup with events is intended only for future occurring events, not past events. Properties include start and end date, duration, ticket details and geolocation. https://developers.google.com/search/docs/data-types/event
Events – the usage of structured data markup with events is intended only for future occurring events, not past events. Properties include start and end date, duration, ticket details and geolocation. https://developers.google.com/search/docs/data-types/event
Video Content – this applies to embedded video content on your website and can be used to indicate duration, license, production company and/or the creator of the video, and even if the content is family friendly.
Music – Google makes provisions for structured data markup for songs and music albums. This can include links to previews of songs, and direct links to buying individual tracks or full albums.


